SAP S/4 HANA Public Cloud & Private Cloud
Inhalt
- SAP S/4HANA On-Premise: The Classic Solution with Full Control
- SAP S/4HANA Private Cloud: Flexibility in the Cloud
- SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud: Standardized, Fast, Scalable
- Migration Packages: GROW with SAP & RISE with SAP
- Key Differences Between SAP S4/HANA Private Cloud and Public Cloud
- Intuitive Business Processes with SAP
- Benefits of Switching to SAP S/4HANA Cloud
- Decision Criteria for Companies
- Conclusion
Inhalt
- SAP S/4HANA On-Premise: The Classic Solution with Full Control
- SAP S/4HANA Private Cloud: Flexibility in the Cloud
- SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud: Standardized, Fast, Scalable
- Migration Packages: GROW with SAP & RISE with SAP
- Key Differences Between SAP S4/HANA Private Cloud and Public Cloud
- Intuitive Business Processes with SAP
- Benefits of Switching to SAP S/4HANA Cloud
- Decision Criteria for Companies
- Conclusion
Definition SAP S/4HANA Public & Private Cloud
SAP S/4HANA is an integrated ERP suite that supports business processes in real time and helps companies work more efficiently. It is based on the SAP HANA in-memory database and can be deployed both locally (on-premise) and in the cloud.
The term SAP S/4HANA Cloud encompasses two different deployment models: the Public Cloud and the Private Cloud. These differ in terms of hosting, maintenance, degree of standardization, and system access, among other things.
SAP S/4HANA forms the digital core of modern IT landscapes. The solution simplifies business processes, offers a modern user interface (Fiori), and supports AI-based analyses. Companies can choose between different operating models depending on their individual IT strategies, regulatory requirements, and budgetary constraints. Before implementation, the key question is therefore: How should SAP S/4HANA be deployed? In addition to the classic on-premise installation, SAP offers two cloud-based variants: the Public Cloud and the Private Cloud.
The differences between these models are significant – technically, economically, and strategically. That’s why we explain:
- what distinguishes the various deployment options
- what advantages and disadvantages each of them entails
- and how companies can choose the right solution based on their individual requirements
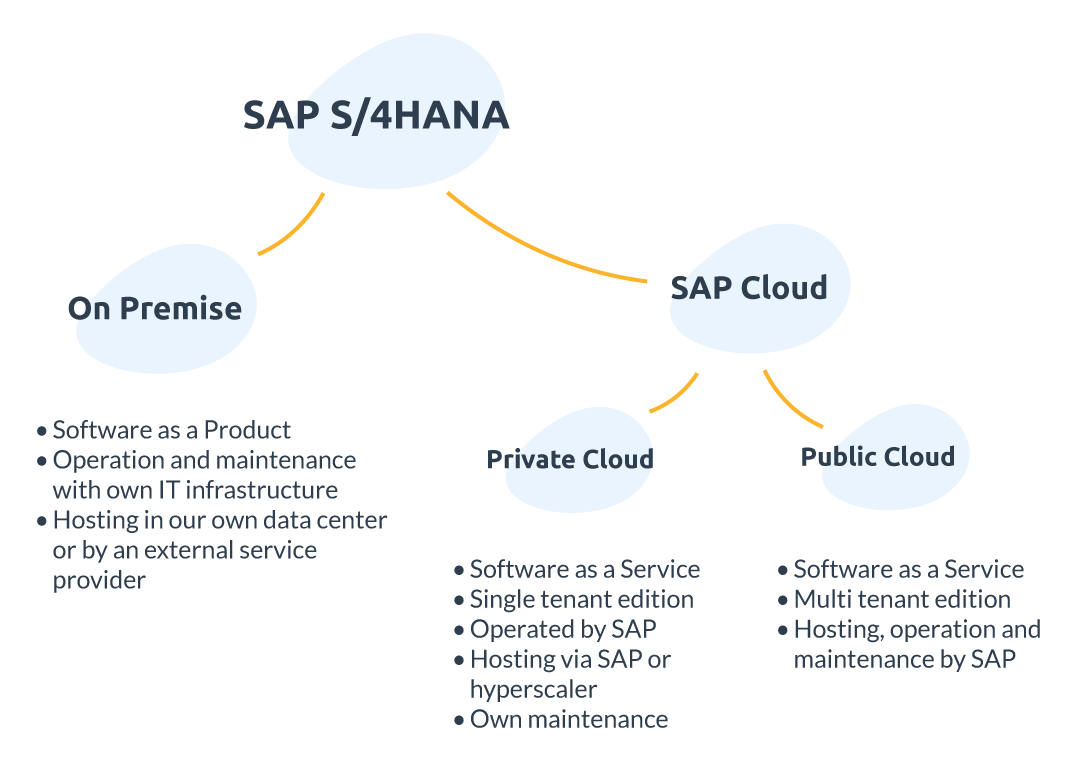
SAP S/4HANA On-Premise: The Classic Solution with Full Control
The on-premise model means that SAP S/4HANA is operated within the company’s own IT infrastructure – either in its own data center or as part of a hosting model provided by an IT service provider.
Advantages:
- Full control over the system, data, and security
- Maximum customizability (customizing, modifications, Z programs)
- No dependence on SAP release cycles (no vendor lock-in)
- Suitable for complex, highly individualized processes
Disadvantages:
- High investment and operating costs
- Longer release cycles (annual)
- Complex updates are the responsibility of your own IT department
- High demands on internal IT expertise
SAP S/4HANA Private Cloud: Flexibility in the Cloud
The Private Cloud (formerly known as “Extended Edition,” “Cloud Ex,” or “Single Tenant Edition”) has been available as part of RISE with SAP since 2021 and combines the advantages of the cloud (e.g., outsourcing of infrastructure, scalable resources) with the flexibility of the on-premise world: Companies receive a dedicated system instance that is operated in a cloud infrastructure (SAP’s own or hyperscalers such as Microsoft Azure, AWS, or Google Cloud Platform). It is often chosen by companies that have higher security requirements or need to map complex business processes
Advantages:
- High adaptability (comparable to on-premise)
- Dedicated instance for full control over security and compliance
- Support for greenfield (new implementation), brownfield (system conversion), and selective migration scenarios
- SAP takes care of operation, maintenance, and infrastructure management
- Faster implementation compared to on-premise
- Updates are your own decision, but required at least every 5 years
Disadvantages:
- Higher costs than Public Cloud
- More complex upgrades compared to Public Cloud
- No full access at system level as with on-premise
SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud: Standardized, Fast, Scalable
The Public Cloud (formerly “Essential Edition,” “Cloud ES,” or “Multi Tenant Edition”; the term SAP S/4HANA Cloud used to refer exclusively to this Public Cloud) is the most modern, purely cloud-based deployment model in the SAP portfolio. It is available via RISE with SAP or – specifically for new customers – via GROW with SAP. The Public Cloud is shared by multiple companies (multi-tenant infrastructure). SAP handles hosting, operation, and maintenance. There are regular updates – comparable to classic SaaS solutions such as Microsoft 365.
This approach enables companies to implement standardized processes and benefit from regular, automatic updates. Extensions are possible, for example, via the SAP Business Technology Platform Extension Suite with public APIs (available in SAP’s Business API Hub). The user interface is a pure SAP Fiori Launchpad. Configurations are made via SSCUIs (Self-Service Configuration UIs), no longer via the classic SAP IMG.
The solution is particularly suitable for companies seeking rapid implementation and lower IT costs. It is also a good option for new SAP customers and those who are completely rebuilding their system.
Vorteile:
- Low initial costs (subscription model)
- Automatic quarterly updates
- High scalability and fast implementation (weeks instead of months)
- Ideal for standardized processes and greenfield implementations
Disadvantages:
- Highly limited customizability
- No full system access
- Dependency on SAP’s update cycles
- Brownfield migrations are not possible
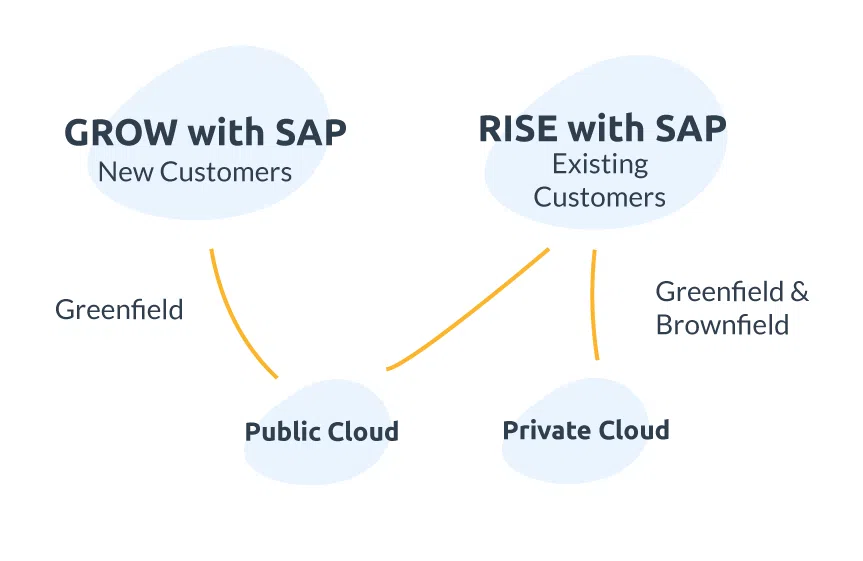
Migration Packages: GROW with SAP & RISE with SAP
SAP offers two migration packages for the transition.
GROW with SAP is aimed at small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that are new to the SAP world and are looking to implement a Public Cloud using a greenfield approach.
RISE with SAP is aimed at existing customers and enables migrations to both Public and Private Clouds – greenfield, brownfield, and selective migration scenarios are possible.
Key Differences Between SAP S4/HANA Private Cloud and Public Cloud
Related Links
Intuitive Business Processes with SAP
Benefits
Benefits of Switching to SAP S/4HANA Cloud
What are the advantages of using a cloud solution? For many companies, switching to SAP S 4HANA Cloud means not only technological renewal, but also a leap forward in innovation toward process automation and increased efficiency.
Cost Control
Thanks to the usage-based pricing model, cloud solutions are often more predictable and cheaper than in-house IT infrastructures—especially in the case of the Public Cloud.
Simplified IT Landscape
Instead of managing dozens of individual solutions, SAP S/4HANA Cloud consolidates processes into one platform—with integrated modules for finance, purchasing, production, sales, and more.
Automation and Workflows
Whether it’s invoice processing, procurement, or customer management, automated processes and workflows are efficient. This is particularly interesting for users of our digital invoice processing solution for SAP.
Access to Innovation
New features, such as AI-supported analyses and predictive capabilities, are rolled out in the Public Cloud first. Those who embrace the cloud early on benefit from regular technological updates.
Scalability
New modules, users, or locations can be quickly activated in the S4HANA Public Cloud—without any major system interventions.
Real-time Data
Thanks to the SAP HANA database, S4HANA Cloud processes large amounts of data in seconds. This enables faster, data-driven business decisions.
Decision Criteria for Companies
The choice between SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud and Private Cloud depends on various factors that should be carefully considered:
-
Business requirements and processes: Companies with standardized processes benefit from the rapid implementation of the Public Cloud. For complex, customized processes, the Private Cloud offers the necessary flexibility.
-
IT resources and expertise: The Public Cloud reduces internal IT costs, as SAP manages the infrastructure. Companies with strong IT departments that want control over their systems may prefer the Private Cloud.
-
Budget and cost structure: The Public Cloud offers a cost-effective subscription model with lower initial investment. The Private Cloud requires higher investment but offers more control over costs in the long term.
-
Security and compliance requirements: Industries with strict regulatory requirements may prefer the Private Cloud in order to meet specific compliance requirements.
-
Growth plans and scalability: Fast-growing companies may benefit from the scalability of the Public Cloud, while established companies with stable processes may choose the Private Cloud.
Conclusion
The decision between SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud and Private Cloud should be based on a thorough analysis of individual business requirements. Both models offer specific advantages and challenges. Companies should consider their business goals, IT strategy, and resources in order to choose the optimal solution.
By carefully weighing the factors mentioned above, companies can make an informed decision that supports their digital transformation and ensures long-term success.
Do you have any questions for us?
We would be happy to advise you during a short, non-binding online appointment!











