The Invoice Verification Checklist for Effective Control of Incoming Invoices
Veröffentlicht am 18.12.2025
Lesedauer: 9 min
Contents
- What is Invoice Verification and Why is it Important?
- What Types of Invoice Verification are There?
- How Should an Invoice be Checked?
- Who is Responsible for Invoice Verification?
- Checklist for Invoice Verification
- Possible Consequences of Incorrect Invoice Verification
- Advantages of Digital Invoice Processing from free-com
- Conclusion
- FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions About Invoice Verification
Inhalt
- What is Invoice Verification and Why is it Important?
- What Types of Invoice Verification are There?
- How Should an Invoice be Checked?
- Who is Responsible for Invoice Verification?
- Checklist for Invoice Verification
- Possible Consequences of Incorrect Invoice Verification
- Advantages of Digital Invoice Processing from free-com
- Conclusion
- FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions About Invoice Verification
Checking incoming invoices is an essential accounting task in any company. It involves checking all the details on incoming invoices to ensure that no incorrect invoices are paid and that only invoices that comply with legal requirements are paid. This is because only invoices that meet the formal requirements of the Value Added Tax Act entitle companies to deduct input tax. This is referred to as factual or content-related and formal invoice verification.
Find out what these terms mean and use our practical invoice verification checklist to check your invoices for completeness.
What is Invoice Verification and Why is it Important?
Invoice verification, also known as incoming invoice verification, is the responsibility of the accounts payable department in large companies. It ensures that incoming invoices meet all criteria in terms of content and form.
Invoices should always be paid only after careful review. This is because invoice verification ensures that the items listed on the invoice actually correspond to the delivery, that quantities and unit prices match the total amount, that the correct tax rate has been applied, and that the payee’s details are correct. In both Germany and Austria, the Value Added Tax Act specifies exactly which formal requirements an incoming invoice must meet in order to be eligible for input tax deduction. In invoice processing, the verification of incoming invoices is therefore an important step that must be carried out carefully.
What Types of Invoice Verification are There?
On the one hand, invoices must correspond to the actual delivery of products or services. This means that the individual items, prices, and data must be correct. On the other hand, there are specific legal requirements that invoices must meet in order to be eligible for input tax deduction. This results in two levels of invoice verification that complement each other.
Substantive invoice verification or content review
The substantive or content-related review of the incoming invoice refers to the verification of all content-related information on the invoice. This includes checking that the list of goods or services delivered is correct and complete, that individual prices, quantities, and totals match, that agreements regarding prices, discounts, rebates, etc. have been complied with, and that the invoice meets internal company requirements.
In order to be able to check the contents of the invoice comprehensively, the incoming invoice should be compared with various related documents. These include, for example, a cost estimate, a quotation, or a delivery note. With free-com’s digital invoice processing, you can save related documents directly and simplify the content-related invoice verification process. Automatic document recognition allows you to read and check all invoice data electronically.
Formal invoice verification
Formal invoice verification refers to the checking of all legally required information on the incoming invoice. Your company can only claim input tax deduction if all the requirements of the sales tax law are met. In both Germany and Austria, input tax deduction is regulated by Section 14 of the respective national sales tax law (UStG). The mandatory information includes the names and addresses of both parties, delivery periods, items and quantities, amounts, any agreements made in advance, bank details, etc. A complete list can be found below, under Checklist for invoice verification.
It makes sense to start the formal invoice verification process immediately after receiving the invoice. This is because compliance with legal requirements is not only important in terms of input tax deduction, but also with regard to a possible audit by the tax office.
What else needs to be considered when conducting a formal and substantive invoice check?
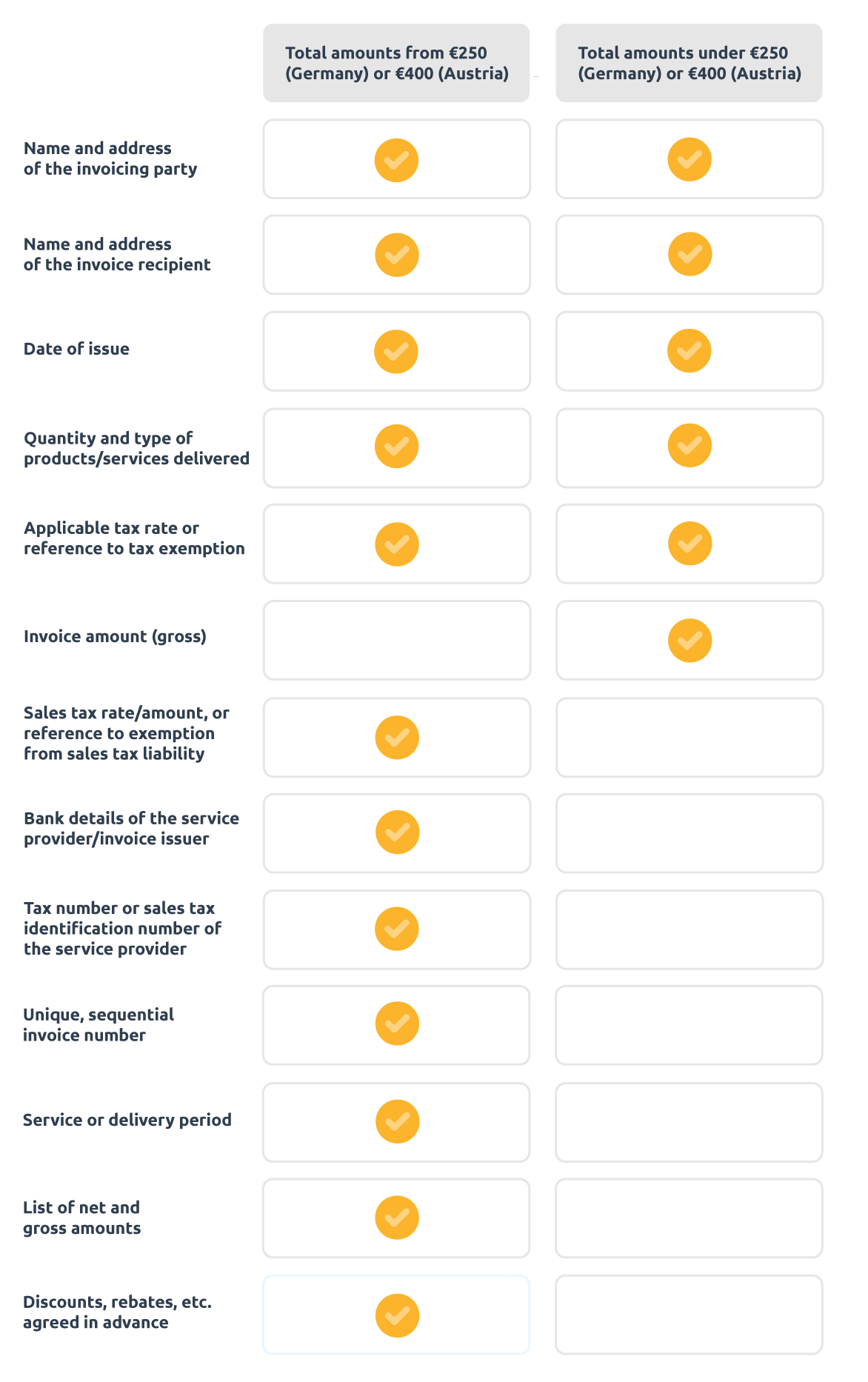
As is often the case, there are exceptions to invoice checking that need to be taken into account. These include, on the one hand, the small business regulation, which allows companies with certain turnover limits to issue invoices without VAT. On the other hand, there is the regulation regarding small amounts. In Germany, the limit according to §33 of the VAT Implementation Regulation (UStDV) is a total amount of EUR 250. In Austria, this limit is a total amount of EUR 400.
Invoices under €250
The big advantage of invoices under EUR 250, or EUR 400 in Austria, is that there are fewer requirements regarding the mandatory information that must be included on the invoice. This serves to reduce the bureaucratic effort involved in invoicing small amounts. The aim is to support SMEs in particular.
In order for small-amount invoices to be legally compliant and valid, they must contain the following information:
- Names and addresses of the service provider/invoice issuer and the service recipient/invoice recipient
- Date of issue
- Quantity and type of products/services delivered
- Invoice amount
- Tax information: sales tax rate, sales tax amount, or reference to exemption from sales tax liability
Invoices over €250
Invoices with a total amount exceeding EUR 250, or EUR 400 in Austria, must contain far more information in order to be eligible for input tax deduction and to be considered audit-proof.
The mandatory information on the incoming invoice is as follows:
- Names and addresses of the service provider/invoice issuer and service recipient/invoice recipient
- Date of issue
- Quantity and type of products/services delivered
- Applicable tax rate or reference to tax exemption
- Tax number or VAT identification number of the service provider
- Unique, sequential invoice number
- Service or delivery period
- Net and gross amount
- Pre-agreed discounts, rebates, etc.
- Bank details of the service provider/invoice issuer
- Consistency between invoice issuer and payee
How Should an Invoice be Checked?
To check incoming invoices efficiently, you should proceed as follows during processing: First, check the formal details for completeness and correctness, then cross-check the content for accuracy, and only release the invoice for payment once the first two steps have been successfully completed.
Only if the formal criteria are met is the invoice eligible for input tax deduction, legally compliant, and therefore audit-proof. If there are already inconsistencies or errors at this stage, any further steps would be a waste of time. If the formal details are correct, proceed to check the content to ensure that you only pay for services that you have actually received. Cross-check with cost estimates, quotes, and delivery notes to verify the products or services ordered and delivered and their agreed prices. Only then can an invoice be released for payment.
Who is Responsible for Invoice Verification?
In large companies, the Accounts Payable Department is usually responsible for invoice verification. The verification process often requires cooperation between different departments, for example to check agreed prices and ordered quantities. Purchasing and Logistics are therefore departments that can play an important role in invoice verification.
Small and medium-sized companies often do not have their own Accounts Payable Department. In such cases, the Financial Accounting Department or the entrepreneur himself assumes responsibility for invoice verification. Practical software solutions help to automate and increase efficiency in the processing of digital incoming invoices. This saves you time and money and minimizes the risk of errors.
Checklist for Invoice Verification
Possible Consequences of Incorrect Invoice Verification
Skipping the invoice verification step can have serious consequences. This is because invoice verification ensures that the company does not suffer any financial damage and that all legal requirements are met. Pay close attention to all details when verifying invoices. Common errors include:
- Formal errors on the invoice
- Incorrect tax rate information
- Calculation errors
- Discrepancies between the order, invoice, and delivery
If a company overlooks these types of errors, it may result in an incorrect invoice being paid and possibly paying for services that were not rendered. This can lead to problems with the tax authorities and a negative working atmosphere with mutual recriminations.
Financially, this can result in damage on several levels:
- No input tax deduction due to incorrect mandatory information
- Increased personnel costs due to time spent on reworking
- Missed discount deadlines
Advantages of Digital Invoice Processing from free-com
The easiest and fastest way to achieve efficient and less error-prone invoice processing is to use a digital solution. Our software for processing incoming invoices uses AI and machine learning approaches to automate even complex layouts and workflows quickly and easily. You benefit from high transparency, clarity, accurate documentation, and user-friendly processes.
Digital invoice processing includes all steps from digital invoice receipt and invoice verification to invoice approval and automatic posting. The system checks all legally relevant invoice characteristics and the consistency of the amounts. Manual checks are only necessary in unclear cases. Thanks to the clear user interface and individual customization options, you can adapt your software solution to your company and your employees. The end result is a digitally processed invoice with transparent documentation of the entire process, including all related documents, as well as audit-proof archiving.
Conclusion
Comprehensive and detailed invoice verification is essential for the correct and error-free processing of incoming invoices. This takes place on two levels: substantive and formal. Formal invoice verification checks whether all legally required information is present. Without this mandatory information or in the event of errors, the input tax deduction entitlement is forfeited. The content or substantive check is primarily for internal operational reasons. Errors in the invoice content, such as in the total amounts or incorrectly calculated discounts, can have a negative financial impact. In times when electronic invoicing is on the rise, a digital solution for invoice processing is an obvious choice. Our user-friendly software uses all the advantages of digital technology to make your invoice processing as efficient and error-free as possible.
Do you have any questions about digital invoice verification? Contact us.
FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions About Invoice Verification
Do you have any questions for us?
We will be happy to consult you during a short, non-binding online appointment!




























